FLIGHT TECHNIQUE — PRO PILOT TECHNIQUES FOR SMOOTH TURNS
If you’ve ever watched a proficient pilot fly (you’ll be able to typically inform by their mirror picture excellent landings), you could have seen how their common flying seems casually routine. In different phrases, they make it look straightforward. That’s as a result of their management of the airplane has develop into largely computerized. For instance, as an alternative of reacting to the airplane each time they carry out a flip, proficient pilots merely repeat the identical flip management inputs and the airplane predictably and constantly follows alongside. By specializing in controlling the airplane and repeating the identical management inputs, you can also expertise the identical predictable outcomes as professional fliers, and subsequently expertise better proficiency in wind, simpler transitions into new and completely different plane sorts, and extra constant touchdown approaches.
PROCEDURE (AILERON) TURNS
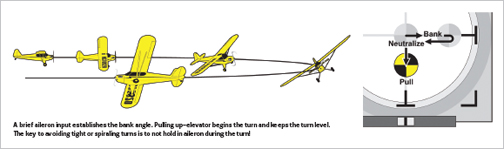
The process that professional pilots use to show most aileron geared up airplanes begins by “setting the financial institution” with a clean, but transient, aileron enter. Note that the aileron enter is neutralized to keep away from pointless changes or coming into a downward spiral, after which up-elevator is utilized to tug the nostril right into a flip and to maintain the flip stage. The flip is then stored stage primarily by adjusting the elevator versus “fiddling” with the ailerons as so many pilots mistakenly do.
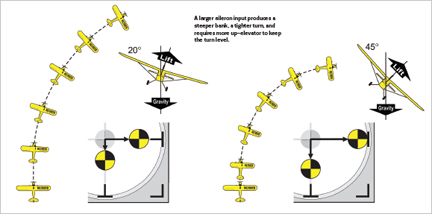
The dimension of the aileron enter determines the diploma of financial institution and subsequently the scale of the flip, in addition to how a lot elevator can be wanted to maintain the flip stage. For instance, a smaller aileron enter produces a shallower financial institution and subsequently a wider flip, whereas a bigger aileron enter produces a steeper financial institution and a tighter flip. The preliminary goal of each proficient pilot is to search out the aileron enter that constantly produces the diploma of financial institution that we’re snug with, after which decide the right amount of elevator to tug every time to maintain the flip stage. You can anticipate that in a gentle financial institution, a lot of the wing’s raise remains to be opposing the pull of gravity, and thus little or no up-elevator can be wanted to maintain the flip stage. During a steeper financial institution, there’s much less upward part of raise to oppose gravity, thus extra up-elevator is required to maintain the flip stage.
CONSISTENT TURNS
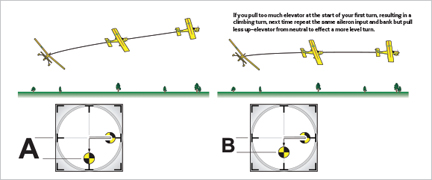
The impartial stick place supplies a definite level from which to gauge the scale of every of our management inputs, subsequently making appropriate quantities simpler to repeat and incorrect quantities simpler to change appropriately. For instance, in case your turns are too tight, reasonably than “fiddling” with the ailerons all through your turns, merely scale back the scale of your preliminary aileron enter from impartial to provide a shallower financial institution and wider turns. Or, for those who initially pull an excessive amount of elevator and execute a climbing flip, repeat the identical aileron enter subsequent time, however pull much less elevator from impartial and the flip can be extra stage.
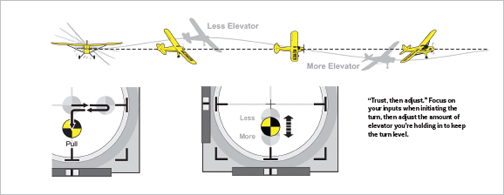
Performing a process flip could be summed up by the motto “Trust, then modify.” That is, proactively provoke your turns trusting your inputs, then modify (fine-tune) the quantity of elevator you’re holding relying on what you see to maintain the flip stage. If you see the airplane begin to lose altitude throughout the flip, pull extra elevator. If the airplane begins to climb, reduce the quantity of elevator that you just’re holding in all through the rest of the flip. Keep in thoughts that as a rule, it’s simpler so as to add extra enter than it’s to get well after over-controlling. Therefore, the very best process is to focus on a small quantity of elevator at the beginning of a flip, after which fine-tune the elevator, if needed, to take care of a wonderfully stage flip.
RESTARTING & TIGHTENING TURNS
In the occasion {that a} flip must be tightened or restarted, the right process is to easily apply a person small bump of aileron (in-out) within the route of the flip to steepen the financial institution angle whereas persevering with to carry within the elevator. Remember, to keep away from over-controlling, the aileron bump must be briefly utilized in-and-out, not held in!
PROCEDURE TURN CORRECTION
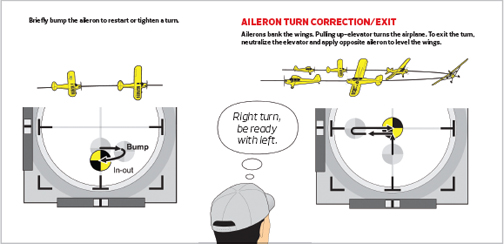
At the purpose that you just wish to exit the flip, neutralize the elevator and easily apply reverse aileron to stage the wings. Note that the important thing to making use of the aileron within the correct route is reminding your self which means you’re turning and anticipating reverse aileron earlier than it’s time to appropriate. The temptation to take a look at the wings to find out which method to apply the aileron produces hesitation and confusion each time the place of the wings is just not clear. Ultimately, appropriately making use of the aileron will hinge on how effectively you begin and keep stage turns, as a result of the much less demanding the flip is normally, the simpler it will likely be to recollect which method to apply the aileron to stage the wings. In reality, so long as the flip was stored stage, you’ll be able to really get away with correcting the mistaken route, catch the error, and stage the wings appropriately with solely minimal altitude loss. On the opposite hand, it may spell doom for an airplane if the pilot corrects the mistaken means throughout a diving flip! Thus, prioritizing elevator changes to maintain every flip stage needs to be the highest precedence for many pilots.
RUDDER TURNS
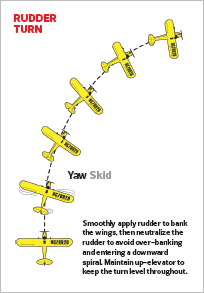
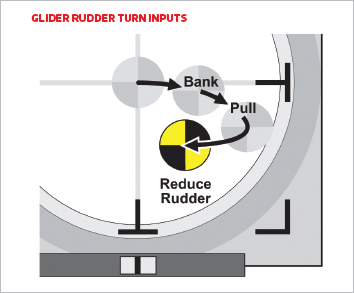
A rudder flip is carried out utilizing the rudder to yaw the nostril of the airplane within the route that you just wish to flip, and whereas area doesn’t allow going into all the main points, most airplanes may also inherently financial institution within the route that the rudder is utilized.
There are mainly two completely different methods required to show an airplane with out ailerons utilizing the rudder. Planes that exhibit numerous upright stability, comparable to a excessive wing powered glider, usually resist banking and subsequently requires you to proceed holding in rudder to maintain turning. These plane usually require a bigger rudder enter to get the flip began, however as soon as began, the rudder needs to be lowered to maintain the flip from changing into too tight. Note: The inherent skid and subsequent velocity loss when making use of rudder will almost certainly require you to mix some up elevator with the rudder at the beginning of the flip to maintain it from dropping.
KEEP IN MIND THAT RUDDER BANKS ARE LESS PRECISE THAN AILERON BANKS AND WILL TEND TO LAG BEHIND YOUR INPUTS IF APPLIED TOO QUICKLY
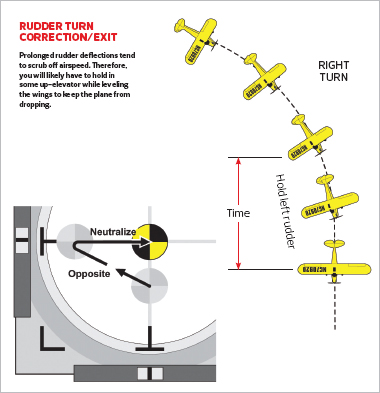
Other rudder planes require a way just like an aileron flip, the place the rudder is utilized solely lengthy sufficient to financial institution the wings, after which it’s neutralized to keep away from over-banking and coming into a downward spiral. Similar to an aileron flip, the diploma of financial institution and the scale of the flip are dictated by the scale of the rudder management enter. Keep in thoughts that rudder banks are much less exact than aileron banks and can are likely to lag behind your inputs if utilized too rapidly. Thus, to realize outcomes that extra carefully match your intentions, it’s essential to apply all of your rudder inputs very easily to provide the airplane an opportunity to maintain up along with your inputs.
Once the flip is began, you’ll want to regulate the elevator to maintain the flip stage, then stage the wings with reverse rudder to exit the flip. Returning the wings to stage often takes longer with rudder than it does with aileron, thus you’ll have to begin leveling the wings previous to the purpose that you really want the flip to cease, after which proceed holding within the rudder till the wings are stage. Note that extended rudder defections and the ensuing skids have a tendency to wash off airspeed, thus you’ll almost certainly want to carry in a little bit up-elevator whereas leveling the wings to maintain the airplane from dropping.
CONCLUSION
Proficient pilots don’t endeavor to get higher at making corrections. Proficient pilots apply management inputs that scale back the necessity for corrections altogether. The key, subsequently, is so that you can take note of making constant management inputs, after which for those who don’t just like the consequence, look to proactively change your inputs/instructions reasonably than react to deviations. Consider that when your flip inputs are made appropriately, the necessity for added corrections could not even exist, and that’s when you can be free to assume forward of the airplane identical to a professional. Good luck and glad flying.
BY DAVID SCOTT, 1ST U.S. R/C FLIGHT SCHOOL

